Introduction: Residential asphalt shingles are a popular roofing material due to their durability, affordability, and aesthetic appeal. However, under certain circumstances, such as exposure to extreme heat, heat blisters may develop on asphalt shingles. This essay aims to explore what heat blisters are, their causes, and potential remedies for homeowners facing this issue.
Definition of Heat Blisters: A heat blister on a residential asphalt shingle refers to a raised or swollen area that forms on the surface of the shingle due to excessive heat exposure. Heat blisters typically appear as small or large bubbles, varying in size from a few millimeters to a couple of inches in diameter.
Causes of Heat Blisters:
- Sun Exposure: Asphalt shingles are designed to withstand a range of weather conditions, including sunlight. However, when exposed to prolonged and intense sunlight, the shingles can absorb an excessive amount of heat, causing the asphalt to soften and form blisters.
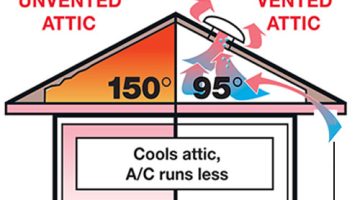
- Inadequate Ventilation: Poor ventilation in the attic or roof space can lead to the accumulation of heat. This trapped heat can radiate through the roof deck and affect the asphalt shingles, contributing to the formation of blisters.
- Improper Installation: Heat blisters can also be a consequence of improper installation techniques. If shingles are not properly fastened or have inadequate adhesive bonds, they may become more susceptible to heat damage.
Effects of Heat Blisters: Heat blisters on residential asphalt shingles can have several detrimental effects:
- Compromised Structural Integrity: As the blisters form, they can weaken the integrity of the shingles, making them more susceptible to damage from wind, rain, or other environmental factors.
- Reduced Aesthetic Appeal: The presence of heat blisters can detract from the visual appeal of the roof. Blisters can create an uneven appearance and give the impression of an aged or poorly maintained roof.
Remedies for Heat Blisters:
- Professional Inspection: Homeowners who suspect heat blisters on their asphalt shingles should consider contacting a professional roofing contractor for a thorough inspection. An expert can assess the extent of the damage and recommend appropriate solutions.
- Ventilation Improvement: Adequate ventilation is crucial to maintaining a stable temperature in the attic or roof space. Installing proper ventilation measures, such as ridge vents, soffit vents, or attic fans, can help dissipate excess heat and reduce the likelihood of heat blister formation.
- Shingle Replacement: In severe cases, where the blisters have compromised the shingles’ structural integrity, replacement may be necessary. Professional roofers can remove the damaged shingles and install new ones, ensuring a secure and visually appealing roof.
- Heat-Reflective Coatings: Applying heat-reflective coatings or cool roof coatings to the asphalt shingles can help reduce heat absorption, minimizing the risk of blister formation. These coatings have reflective properties that deflect sunlight and lower the overall temperature of the roof surface.
Conclusion: Heat blisters on residential asphalt shingles can be a cause for concern among homeowners. Understanding their causes and effects is essential in effectively addressing this issue. By implementing preventive measures, such as improving ventilation and using heat-reflective coatings, homeowners can mitigate the risk of heat blister formation and maintain the longevity and aesthetic appeal of their asphalt shingle roofs. In cases where damage has already occurred, consulting with a professional roofer for inspection and potential replacement is advisable to ensure the integrity of the roof is preserved.